Humanoids & Invasion of Privacy
HomeHumanoids & Invasion of Privacy
.jpg)
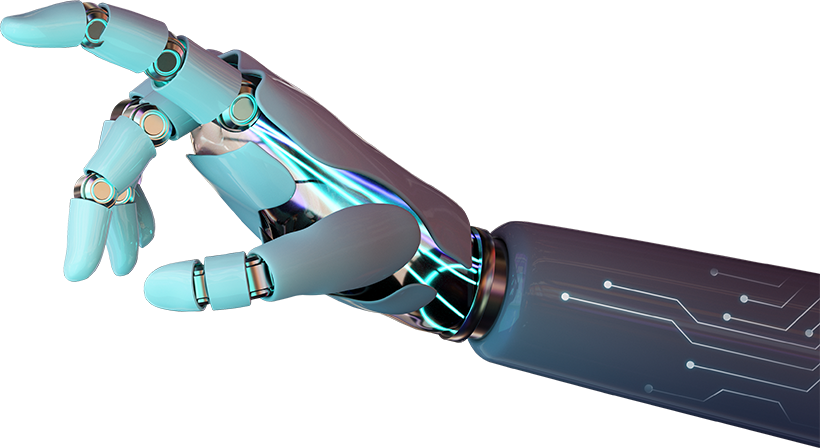
Humanoids are sophisticated robotic systems designed to replicate human form and behaviour, enabling them to perform tasks traditionally carried out by people. Unlike conventional robots that are often limited to industrial or repetitive functions, humanoids are equipped with artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced sensory capabilities. These features allow them to navigate dynamic environments, interact naturally with humans, and adapt to new tasks. Their growing role in society is evident in industries such as healthcare, retail, security, and logistics, where they assist with customer service, elder care, and hazardous work environments. As their presence expands, humanoids are becoming integral to enhancing efficiency and productivity across various sectors.
However, as humanoids become more embedded in daily life, privacy concerns have emerged as a significant challenge. These AI-driven systems often collect vast amounts of personal data through cameras, microphones, and biometric sensors to operate effectively. While this enables them to provide personalized services, it also raises concerns about data security, surveillance, and potential misuse of sensitive information. The integration of humanoids in public and private spaces calls for robust legal and ethical frameworks to ensure responsible data handling and user protection. This article will explore the evolution of humanoids, their impact on society, and the privacy implications associated with their widespread adoption, emphasizing the need for regulatory safeguards in the age of Artificial intelligence (AI) -driven robotics.
.jpg)
The rise of humanoids in daily life marks a transformative era where AI and robotics are seamlessly integrated into various aspects of society. In homes, humanoid robots enhance convenience by automating household tasks and providing companionship, especially for elderly individuals or those with disabilities. In workplaces, these robots are revolutionising industries by performing repetitive or hazardous tasks, improving efficiency, and enabling human-robot collaboration. Their ability to mimic human behaviour makes them ideal for customer service roles, where intuitive interactions are crucial. Healthcare is another area witnessing significant advancements; humanoids equipped with AI assist in telemedicine, patient monitoring, and caregiving, alleviating the burden on healthcare professionals and ensuring better patient outcomes.
Public spaces are increasingly adopting humanoids for surveillance and security purposes, leveraging their ability to analyze environments and respond to potential threats autonomously. In caregiving scenarios, AI-driven humanoids provide personalized support by predicting health issues and intervening before emergencies arise. These robots also play a pivotal role in customer service across industries, offering 24/7 assistance, managing inquiries, and streamlining workflows. The increasing autonomy of humanoids in decision-making is reshaping their role from mere assistants to proactive problem-solvers capable of adapting to dynamic environments. This autonomy is powered by advanced machine learning algorithms that enable them to interpret human emotions and social cues, fostering more natural interactions.
As humanoids become smarter and more intuitive, their integration into daily life raises profound ethical and societal questions. While they promise unprecedented efficiency and convenience, challenges such as data privacy, reliability in critical situations, and the displacement of human jobs demand careful consideration. Nonetheless, the ongoing development of humanoid robots signals a future where they are indispensable partners in enhancing human life across diverse domains.
.jpg)
Humanoids, equipped with advanced AI and robotics, are increasingly integrated into daily life, raising significant privacy concerns. These robots collect vast amounts of personal data through cameras, microphones, and sensors embedded in their systems. For instance, household robots like robotic vacuums map homes, while humanoids in public spaces gather information about individuals’ movements and interactions. This constant surveillance creates opportunities for sensitive data to be exploited, whether by the manufacturers or unauthorized entities. The anthropomorphic design of humanoids often disarms users, making them less cautious about the data they share, further exacerbating privacy risks.
Facial recognition and biometric technologies used by humanoids amplify ethical concerns surrounding privacy. These systems can identify and track individuals without their consent, leading to potential misuse of personal information. For example, facial recognition could be employed to analyse purchasing habits or even credit scores without informing users, as seen in some retail environments. Moreover, the storage of biometric data in centralized databases makes it an attractive target for cybercriminals. A breach could expose sensitive information, such as facial templates or fingerprints, which are irreplaceable once compromised.
As humanoid robots become more integrated into everyday life, ensuring the security of the data they collect is a major concern. Weak encryption protocols and vulnerabilities in storage mechanisms make them potential targets for cyberattacks. Key concerns include:
Adding to these concerns is the lack of transparency in how humanoids process and use collected data. Users often remain unaware of what information is being gathered or how it is utilized. This opacity undermines trust and raises ethical questions about informed consent. Transparency could help users understand the robot’s goals and behaviours, but excessive complexity in explanations might overwhelm them. Striking a balance between transparency and usability is essential for ensuring that humanoids are both effective and ethically sound.
.jpg)
The integration of humanoid robots into society raises complex legal and ethical concerns, especially regarding privacy, accountability, and consent. Existing data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, provide frameworks for protecting personal data. However, their applicability to humanoid technology remains ambiguous. These laws were designed for traditional data collection systems and may not fully address the unique challenges posed by humanoids, which gather data through cameras, microphones, and sensors embedded in everyday environments. For instance, a humanoid robot in a public space might inadvertently collect biometric data or record private conversations without explicit user consent, raising questions about whether such actions fall within the scope of existing regulations.
Ethical dilemmas surrounding consent and AI-driven surveillance further complicate the deployment of humanoids. Unlike traditional devices, humanoid robots often operate autonomously and interact with humans in ways that blur the boundaries of informed consent. For example, a humanoid equipped with facial recognition technology might track individuals without their knowledge or approval, creating significant ethical concerns about surveillance and profiling. Additionally, the anthropomorphic design of humanoids can lead to misplaced trust, where users unknowingly share sensitive information with machines that lack transparency about how this data will be processed or stored. These dilemmas demand robust ethical guidelines to ensure that humanoid technologies respect individual rights and do not exploit vulnerabilities in human behaviour.
Accountability is another critical issue in cases where humanoids breach privacy or cause harm. Determining responsibility—whether it lies with developers, manufacturers, or users—is a contentious debate. Developers may be held accountable for programming flaws that enable unethical behaviours, while manufacturers could face scrutiny for inadequate security measures or misleading marketing claims about their products’ capabilities. Users also are responsible for deploying humanoids in ways that may infringe on others’ privacy. However, the autonomous nature of these machines complicates this issue further; if a humanoid makes an independent decision that leads to harm, assigning liability becomes challenging. Clear legal frameworks are needed to establish accountability across all stakeholders to prevent misuse and ensure ethical deployment of humanoid technologies.
.jpg)
Recent years have seen several notable privacy breaches involving humanoid robots, highlighting the growing concerns surrounding their integration into daily life. In 2022, a curious traveller at an airport saw a robot helping with onboarding. On digging into the working style and other details of the robot, it was found that the companies involved in making the robot didn’t even have a well-drafted privacy policy for the robot. Similarly, in 2023, a humanoid robot deployed in a shopping mall was discovered to be using facial recognition technology to track customers' movements and purchasing habits without their knowledge, raising serious questions about consent and data protection.
Cases of AI misidentification and wrongful surveillance have also emerged, further fuelling public scepticism about humanoid robots. In a particularly troubling incident in 2025, a security robot in a residential complex mistakenly identified several residents as intruders, leading to unnecessary confrontations and privacy violations. This event, along with others like it, prompted a significant public backlash and calls for stricter regulation of AI-powered surveillance systems. In response, several countries have begun implementing new laws specifically addressing the use of humanoid robots in public spaces, with a focus on transparency, consent, and data protection. These regulatory efforts aim to strike a balance between technological innovation and individual privacy rights, though the rapidly evolving nature of humanoid robotics continues to present challenges for policymakers and ethicists alike.
.jpg)
Mitigating the privacy risks associated with humanoid robots requires a multi-faceted approach that combines technological innovation, regulatory updates, and user empowerment.
Looking ahead, achieving a balance between innovation and ethical responsibility will be crucial as humanoid technologies continue to evolve. Developers must prioritise ethical AI practices, such as bias-free algorithms and transparent decision-making processes while fostering collaboration between technologists, policymakers, and ethicists to address emerging challenges. By combining privacy-focused design, robust legal protections, and informed user participation, society can harness the benefits of humanoid robots without compromising individual rights or trust in these transformative technologies.
The rapid integration of humanoid robots into society presents a paradox: while they offer immense benefits in automation, efficiency, and convenience, they also introduce significant privacy and ethical challenges. As these AI-driven systems continue to evolve, their ability to collect, process, and store personal data raises critical concerns about surveillance, consent, and data security. The vulnerabilities associated with humanoids—ranging from unauthorized data collection to potential misuse by cybercriminals—underscore the urgency of addressing privacy risks through a combination of technological, legal, and ethical measures.
To ensure a responsible and secure future for humanoid robotics, a multi-pronged approach is essential. Privacy by Design principles must be embedded into development processes, and robust regulatory frameworks need to be adapted to the autonomous nature of these systems. Public awareness and transparency in data usage will also play a pivotal role in building trust and ensuring informed user participation. Ultimately, striking a balance between innovation and ethical responsibility will determine the societal acceptance and long-term viability of humanoid robots. By prioritizing security, accountability, and human-centric AI governance, we can harness the full potential of humanoids while safeguarding individual rights and privacy.
We at DataSecure (Data Privacy Automation Solution) can help you to understand Privacy and Trust while lawfully processing the personal data and provide Privacy Training and Awareness sessions in order to increase the privacy quotient of the organisation.
We can design and implement RoPA, DPIA and PIA assessments for meeting compliance and mitigating risks as per the requirement of legal and regulatory frameworks on privacy regulations across the globe especially conforming to GDPR, UK DPA 2018, CCPA, India Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023. For more details, kindly visit DPO India – Your Outsourced DPO Partner in 2025.
For any demo/presentation of solutions on Data Privacy and Privacy Management as per EU GDPR, CCPA, CPRA or India Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023 and Secure Email transmission, kindly write to us at info@datasecure.ind.in or dpo@dpo-india.com.
For downloading various Global Privacy Laws kindly visit the Resources page in Resources.